« Syllabus » : différence entre les versions
| (6 versions intermédiaires par 2 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 5 : | Ligne 5 : | ||
== Interaction with VR and AR Environments (IEVA) == | == Interaction with VR and AR Environments (IEVA) == | ||
=== Teachers === | === Teachers === | ||
[mailto:anne-gwenn.bosser@enib.fr Anne-Gwenn Bosser] (In charge, ENIB), | [mailto:anne-gwenn.bosser@enib.fr Anne-Gwenn Bosser] (In charge, ENIB), Maxim Spur, Elisabetta Bevacqua, Olivier Augereau, Pierre De Loor, Eric Maisel | ||
=== Number of hours and ECTS === | === Number of hours and ECTS === | ||
| Ligne 94 : | Ligne 94 : | ||
== Modelling, design and usability of interactive systems (MCSI) == | == Modelling, design and usability of interactive systems (MCSI) == | ||
=== Teachers === | === Teachers === | ||
[mailto:sebastien.kubicki@enib.fr Sébastien Kubicki] (In charge, ENIB), Cédric Fleury, Charlotte Hoareau | [mailto:sebastien.kubicki@enib.fr Sébastien Kubicki] (In charge, ENIB), Cédric Fleury, Charlotte Hoareau, Elodie Bouzekri | ||
=== Number of hours and ECTS === | === Number of hours and ECTS === | ||
| Ligne 125 : | Ligne 125 : | ||
== Interactive Machine Learning (IML) == | == Interactive Machine Learning (IML) == | ||
=== Teachers === | === Teachers === | ||
[mailto: | [mailto:mihai.andries@imt-atlantique.fr Mihai Andries] (in charge, IMT-A), Pierre de Loor (In charge, ENIB), Antoine Dizet. | ||
=== Number of hours and ECTS === | === Number of hours and ECTS === | ||
| Ligne 140 : | Ligne 140 : | ||
=== [https://www.enib.fr/~buche/data/IML/ Link toward the numerical space of the module]=== | === [https://www.enib.fr/~buche/data/IML/ Link toward the numerical space of the module]=== | ||
== Conferences == | == Conferences (Ouverture Scientifique)== | ||
[mailto:jriviere@univ-brest.fr Jérémy Rivière] (in charge, UBO) | [mailto:jriviere@univ-brest.fr Jérémy Rivière] (in charge, UBO) | ||
| Ligne 169 : | Ligne 169 : | ||
== Préparation à la Vie Professionnelle (PVP) == | == Préparation à la Vie Professionnelle (PVP) == | ||
=== Teachers === | === Teachers === | ||
[mailto:mounir.lallali@univ-brest.fr Mounir Lallali] (In charge of the Industry part, UBO), [mailto: | [mailto:mounir.lallali@univ-brest.fr Mounir Lallali] (In charge of the Industry part, UBO), [mailto:vidalenc@univ-brest.fr Nicolas Vidalenc] (in charge of the Communication part, UBO), [mailto:pierre-emile.laperine@univ-brest.fr Pierre-Emile Laperine] (in charge of the English part, UBO). | ||
=== Volume horaire et ECTS === | === Volume horaire et ECTS === | ||
| Ligne 210 : | Ligne 210 : | ||
== Stages == | == Stages == | ||
=== Intervenants === | === Intervenants === | ||
[mailto: | [mailto:pascal.ballet@univ-brest.fr Pascal Ballet] (In charge, UBO). | ||
=== ECTS === | === ECTS === | ||
Dernière version du 19 juillet 2024 à 07:09
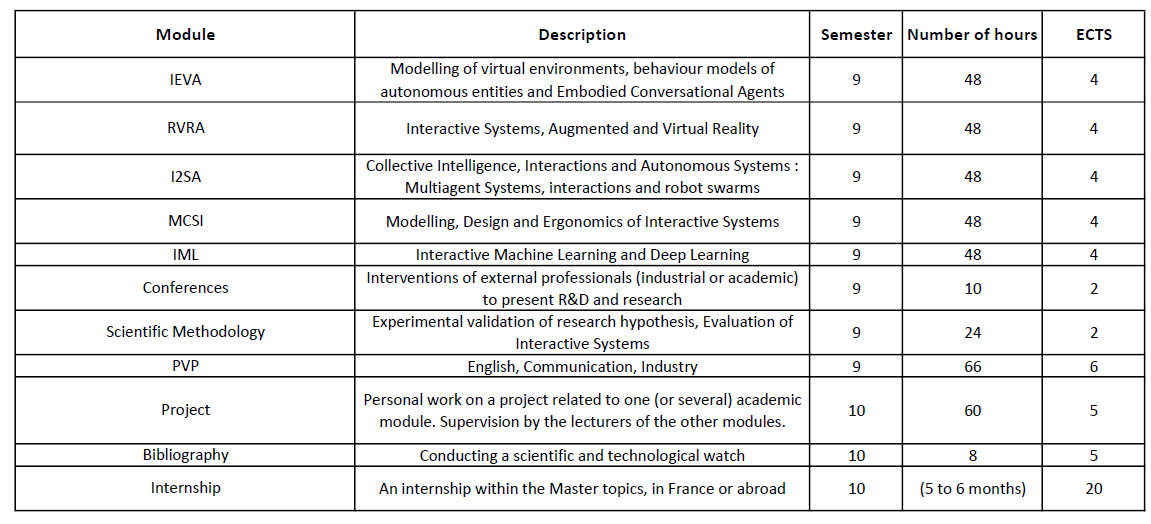
Semester 9
Interaction with VR and AR Environments (IEVA)
Teachers
Anne-Gwenn Bosser (In charge, ENIB), Maxim Spur, Elisabetta Bevacqua, Olivier Augereau, Pierre De Loor, Eric Maisel
Number of hours and ECTS
48h CM-TP. 4 ECTS.
Presentation
The course concerns models, methods and tools for the synthesis of interactive virtual environments. It begins with an introduction to virtual environment development with Unity coupled with a more lectured course in game studies. This is followed by independent and research-informed course sections on content creation for virtual environments, including adaptive content: animated conversational agents, procedural generation techniques, user modelling and adaptation to user profiles and behaviour.
Objectives
3D Ludology
- Introduction to game design (elements of ludology, interactive narration, notion of playability and engagement factors, game mechanics)
- Unity 3D project
Procedural content generation
- Generation techniques: based on AI, combinatorics. Content curation.
- Illustration for specific areas (objects, game levels, quests, text and dialogue, music...)
Autonomous interactive entities, such as characters (virtual humans) Adaptive interactive environments
- From adaptation to co-construction
- Serendipity, autonomy
- Embodiment of information
- User profile identification
- Domain model
Affective modelling: physiological and behavioural measures
- Affect detection, biofeedback, subjective evaluation
- CM eye movement analysis
- Introduction to physiological signals (EDA, BVP, EMG, EOG, ECG...)
- Practical work: webgazer, tobii, empatica
Link toward the numerical space (Moodle) of the module
Virtual and Augmented Reality (RVRA)
Teachers
Cédric Fleury and Etienne Peillard (In charge, IMT-A), Thierry Duval
Number of hours and ECTS
48h CM-TP. 4 ECTS.
Presentation
This course aims to give the basics of the creation and use (especially collaborative) of Virtual and Augmented Reality environments. It also focuses on the problems that can be encountered in AR and the solutions proposed.
Objectives
Addressing the basic principles of Virtual and Augmented Environments
- VR-AR technologies
- 3D Modelling / Blender and 3D Rendering / Shader
Introduction to the principles of interaction in Virtual and Augmented Environments
- 3D Interaction
- 3D Navigation
- Human factors (Immersion, Perception, Cybersickness, ...)
Overview of Augmented Reality techniques
- Optical see through
- Video see through
- Projective
Addressing virtual shared environments and multi-user interactions
Link toward the numerical space (Moodle) of the module
Collective Intelligence, Interaction and AutonomousSystems (I2SA)
Teachers
Pascal Ballet (In charge, UBO), Gilles Coppin, Jérémy Rivière, Aymeric Hénard.
Number of hours and ECTS
48h CM-TP. 4 ECTS.
Presentation
This module is interested in the notion of autonomy, and in particular the autonomy of complex systems, composed of many interacting parts. The main algorithms for self-organisation of these systems are addressed through Multi-Agent Systems, as well as the different methods of interaction between them and a human user. These methods and algorithms are implemented in simulation platforms as well as with real swarms of robots.
Objectives
Studying autonomous systems
- Concept of autonomy, autonomous system
- Level of autonomy of a system, Sheridan
- Human Autonomy Teaming
Studying Multi-Agent Systems
- MAS for simulation
- Principles of reactive (complexity etc.) and cognitive self-organisation
- Main self-organisation algorithms
- Interactions with agent-based simulations
- Considering swarms of robots
- Autonomous robotics
- Main self-organisation algorithms
- Human - Robot Swarm Interaction
Link toward the numerical space (Moodle) of the module
Modelling, design and usability of interactive systems (MCSI)
Teachers
Sébastien Kubicki (In charge, ENIB), Cédric Fleury, Charlotte Hoareau, Elodie Bouzekri
Number of hours and ECTS
48h CM-TP. 4 ECTS.
Presentation
This course aims at introducing the general concepts related to HMI (Human Machine Interaction) and the User-Centered Design approach. It includes the human factors to be taken into account when designing HMIs, the different existing interaction techniques, as well as the analysis and evaluation of the user experience.
Objectives
HMI and Ergonomics basics Human factors
- Introduction to cognitive psychology and its contribution to UCD
- Human cognitive architecture: limits of memory and consideration in design
- Perception: information processing systems
- Attentional model: taking into account the limited attention of users during design
Modelling (architectures, interaction patterns...) Interaction techniques (multimodal interactions) Ergonomics (digital / web / interaction)
- Link between human factors and ergonomics
- Heuristics
- Expert evaluation
- Experience map
Evaluation of user experience
- Usability scales
- User testing
- Mock-up
Link toward the numerical space (Moodle) of the module
Interactive Machine Learning (IML)
Teachers
Mihai Andries (in charge, IMT-A), Pierre de Loor (In charge, ENIB), Antoine Dizet.
Number of hours and ECTS
48h CM-TP. 4 ECTS.
Presentation
Interactive Machine Learning (IML) merges machine learning and human-computer interaction. While traditional machine learning systems process the data that have been given to them in advance, this course considers that the learning process could benefit from interactions with the environment as well as with a human, and that inputs and outputs from and for humans carry meaningful information. Indeed humans may provide input to a learning algorithm, including inputs in the form of labels, demonstrations, advice, rewards or rankings. The interaction is all the more useful as the human can guide along the learning process while adapting his guidance to the outputs of the algorithm. This interaction can be in the form of feedforward or feedback information. The timing of these interactions can be preset, left to the teacher’s initiative or even to the learner’s initiative. In the latter case, the algorithm called “active learner" can decide when, about what, how and with whom to interact to optimise its learning process. Thus a bidirectional dialogue can emerge. Application will focus on interactive robot programming covering topics including sensing in real-world environments, mapping, navigation, localization, kinematics and vision. Students will program virtual and physical robots interacting with the world using modern Robot Operating System.
Objectives
- Interactive Machine learning
- Interactive Robotic
- Interactive Machine Learning for Robotic
Link toward the numerical space of the module
Conferences (Ouverture Scientifique)
Jérémy Rivière (in charge, UBO)
Number of hours and ECTS
10h Conferences. 2 ECTS.
Presentation
This module offers a general scientific culture, through a series of research presentations and meetings with innovation professionals.
Scientific Methodology
Teachers
Pierre De Loor (In charge, ENIB), Gilles Coppin.
Number of hours and ECTS
24h CM-TP. 2 ECTS.
Presentation
This course focuses on methods of experimental validation of a research hypothesis, and evaluation of interactive systems
Objectives
Addressing the main human-experience models
- The currents of cognitive science (behaviourism, cognitivism, constructivism, connectionism)
- Models, tools and associated methods
- Statistical models and behavioural approaches: statistical processing of results, hardware or software impact, surveys, making relevant curves
Link toward the numerical space (Moodle) of the module
Préparation à la Vie Professionnelle (PVP)
Teachers
Mounir Lallali (In charge of the Industry part, UBO), Nicolas Vidalenc (in charge of the Communication part, UBO), Pierre-Emile Laperine (in charge of the English part, UBO).
Volume horaire et ECTS
72h CM-TD. 6 ECTS.
Semester 10
Project
Teachers
Jérémy Rivière (In charge, UBO).
Number of hours and ECTS
2 weeks. 5 ECTS.
Presentation
The Project module aims at reinforcing the preparation for professional integration of the students. It consists in carrying out an IT project in connection with an academic module and one (or several) tool(s).
- Each year, 2-3 project subjects in relation with each academic module: IML, SMA, IEVA, MCSI, RVRA. The students choose a project according to their specialization objective.
- The project lasts 10 full days (2 weeks)
- The projects are supervised by the teachers who submitted the subjects
- At the end of the project, the students must provide a written report and make an oral presentation of their work.
Objectives
- Deepen technical knowledge
- Implementing theoretical knowledge
- Develop autonomy, teamwork
- Increase experience in oral and written communication
Bibliography
Teachers
Jérémy Rivière (In charge, UBO).
Number of hours and ECTS
4h TD. 5 ECTS.
Presentation
This module develops the ability to carry out a state of the art or a technology watch on a scientific question or an innovation problem. It also presents the techniques for writing a scientific article according to international standards, and for presenting the work orally. The work consists in carrying out a bibliographical research with the appropriate tools, then to write a document presenting this state of the art (scientific or technological). The study must present in a synthetic and critical way the existing solutions and compare them.
Link toward the numerical space (Moodle) of the module
Stages
Intervenants
Pascal Ballet (In charge, UBO).
ECTS
20 ECTS.
Presentation
An internship within the Master topics, in France or abroad, for 5 to 6 months.